For example: in the below structure when cell divide again and give the same number of chromosome same is called……….
a) Meiosis I
b) Meiosis II
c) mitosis
d) none of these
Meiosis I is reductional division and meiosis II is equational division because of
a) Separation of chromatids
b) Crossing over
c) The disjunction of homologous chromosomes
d) The pairing of homologous chromosomes
(Prophase I) important concept:
Prophase I is divided into 5
distinctive sub-stages:
Leptotene: The chromosomes begin to
condense and are attached to the nuclear membrane via their telomeres
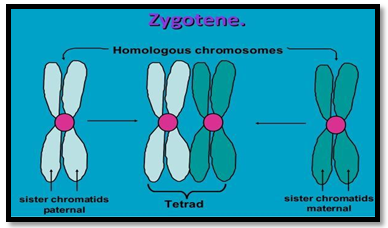
Zygotene: Synapsis begins with a
synaptonemal complex forming between homologous chromosomes
Pachytene: Crossing over of genetic
material occurs between non-sister chromatids
Diplotene: Synapsis ends with
disappearance of synaptonemal complex; homologous pairs remain attached at
chiasmata
Diakinesis: Chromosomes become fully
condensed and nuclear membrane disintegrates prior to metaphase I
When homologous pairs come closer
together is called……….
a) Leptotene
b) Zygotene
c) Pachytene
d) Diakinesis
Synapsis takes place between…………..
a) Spindle fiber and centromere
b) mRNA and ribosomes
c) a female and a male gamete
d) Two homologous chromosomes
Pairing of homologous chromosomes can be seen during……….
a) Leptotene
b) Zygotene
c) Pachytene
d) Diakinesis