

Force and Machine (old version text book)
1) Friction: Friction is a force which opposes
motion.
2) Machine is devices which helps us in doing our work and make
our life easier.
3) Causes of friction: All solid materials have some roughness. This
roughness causes friction.
4) Mass: 1) Mass is the quantity of matter in an object. 2)
Mass remain same everywhere.
5) Weight: 1) The gravitational force acting on an object is
called its weight. 2) Weight does not
remain the same everywhere.
6) Friction helps us in walking and running.
7) Friction prevents the vehicle from skidding.
8) Moving
objects slow down due to friction.
9) Friction causes wastage of energy.
10) Gravitational force is the force of attraction
that pulls all objects towards the center of the earth.
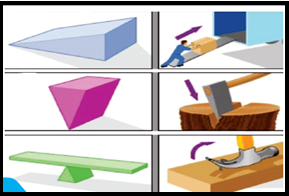
11) The
claw hammer is an example of class lever.
12) The SI unit of force is Newton
(N).
13) The
unit of Mass is Kg.
14) Lever is one of the simplest types of machine which helps us to do work
more easily.
15) Kinds of liver: Liver is classified in to three classes based on
relative position of the Fulcrum (F), the Effort (E), and the Load (L).
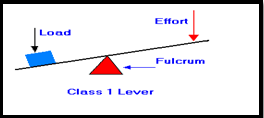
16) Lever of class I: In first class lever, the fulcrum is between the effort
and the load. Examples Scissors, claw hammer and sea saw.
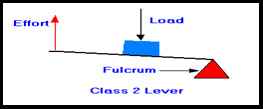
17) Lever of Class II: In the second lever, the load is between the fulcrum
and the efforts. Examples Bottle opener, wheelbarrow, etc.
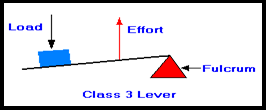
18) Lever of Class III: In third class lever the
efforts is between the fulcrum and the load. Examples, Stapler, human arm, fishing
rod.
19) Balance forces are equal and opposite in direction.
20) Wedges and inclined planes are simple machines which are frequently used
in daily life.
MCQs
Unite of force in SI is………………
a) Meter
b) Pound
c) Kilogram
d) Newton
Ball bearings reduce friction because they……
a) Reduce roughness of surface
b) Roll on surface to reduce friction
c) Increase the surface area in contact
d) Heat up the surface area in contact
A sharpener is an example of…………………
a) Lever
b) Wedge
c) Inclined Plane
d) Inertia
The quantity of matter present in an object is it’s……………..
a) Density
b) Weight
c) Mass
d) Volume