Circuits and Electric Current
The flow
of electron current I=Q/t The
unit current amperes or amps.
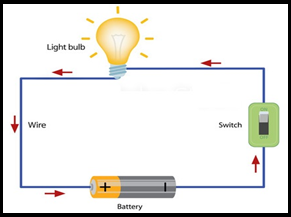
The complete path for the flow of current through the wire the cell and the
filament of the bulb are called circuit
A series circuit one path Parallel circuit separate paths
An electric circuit is a complete unbroken path through which electric current
can flow, such a circuit is called closed circuit.
When there is no break in a circuit, no electric current is flow; such type
circuit is called open circuit.
A light bulb electric energy light
energy
A radio electric bells sound energy
A fan electric energy mechanical
energy
The chemical effect of current The difference
in electrical potential of the charge is called the potential difference
or voltage. The
difference in electrical potential is called voltage (V) V=
W/Q The
unit voltage volt Alessandro
Volta who invented the first chemical battery The
opposition to the flow of current is called resistance. Resistance is represented
by “R” ohms (Ω). A component close or break switch A component which provides resistance is called resister. The
relationship between voltage, current, and resistance according to Ohm’s
law……………… Voltage (V) = Currant
(I) ×
Resistance (R) An ammeter measure current. Voltmeter voltage. Miniature circuit breakers (MCB) automatically switches
off abnormal condition A fuse safety device low
melting A fuse is used to………………………..
Show answer
c
Comments
The earth wire…………………………. Prevent electrical shocks
Show answer
b
Comments
Charge in motion produces…………….
Show answer
a
Comments
Current represent by symbol ………..
Show answer
c
Comments
The unit of current is ……...
Show answer
a
Comments