

Respiratory and Circulatory
The circulatory and respiratory systems work together to circulate blood
and oxygen throughout the body. Air moves in and out of the lungs through the
trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles. Blood moves in and out of the lungs through
the pulmonary arteries and veins that connect to the heart.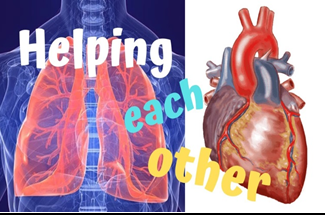
Which of the
following is required for doing different functions?
a) water
b) oxygen
c) energy
d) food
Explanation:energy, in physics, the capacity for doing work. It may exist in potential, kinetic, thermal, electrical, chemical, nuclear, or other various forms. There are, moreover, heat and work i.e., energy in the process of transfer from one body to another.
In case of us, from where does the energy to perform all the body functions?
a) from water we drink
b) from sun
c) from food we eat
d) from soil
The food we eat is broken down and converted into smaller molecules of ………
a) glucose
b) glycogen
c) starch
d) chitin
Explanation:Glucose comes from the Greek word for "sweet." It's a type of sugar you get from foods you eat, and your body uses it for energy. As it travels through your bloodstream to your cells, it's called blood glucose or blood sugar. Insulin is a hormone that moves glucose from your blood into the cells for energy and storage.
Which of the following is/are the major source of energy for the cell?
a) water
b) glucose
c) proteins
d) all of these
Which of the following process is involved in the release of energy from food?
a) photosynthesis
b) combustion
c) cellular respiration
d) rusting
Explanation:Cellular respiration is a series of chemical reactions that break down glucose to produce ATP, which may be used as energy to power many reactions throughout the body. There are three main steps of cellular respiration: glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation.