

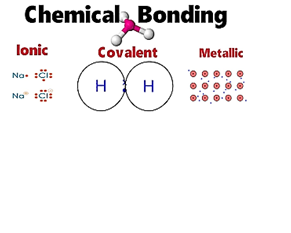
Chemical BONDS
A chemical
bond is a lasting attraction
between atoms, ions or molecules that enables the
formation of chemical compounds. The bond may result from
the electrostatic force between oppositely charged ions as in ionic
bonds or through the sharing of electrons as in covalent bonds. The
strength of chemical bonds varies considerably; there are "strong
bonds" or "primary bonds" such as covalent, ionic and metallic
bonds, and "weak bonds" or "secondary bonds" such
as dipole–dipole interactions, the London dispersion force and hydrogen
bonding.
Elements
combine together to form………
a) shells
b) orbits
c) bonds
d) energ
Explanation:A chemical bond is a lasting attraction between atoms, ions or molecules that enables the formation of chemical compounds. The bond may result from the electrostatic force between oppositely charged ions as in ionic bonds or through the sharing of electrons as in covalent bonds.
The combining capacity of the atom to form a chemical bond is
called…….
a) reactivity
b) valency
c) capacity
d) all of these
Explanation:In chemistry, the valence or valency of an element is the measure of its combining capacity with other atoms when it forms chemical compounds or molecules.valence, also spelled valency, in chemistry, the property of an element that determines the number of other atoms with which an atom of the element can combine. Introduced in 1868, the term is used to express both the power of combination of an element in general and the numerical value of the power of combination.
The valency of an element is the number of electrons its atom………to form compound?
a) gains
b) loses
c) shares
d) all of these
Valency of an atom is always……..
a) small whole number
b) zero
c) decimal fraction
d) both a and b
Which of the following element/s does/do not form compound?
a) elements having valency 1
b) elements having valency 2
c) elements having valency 3
d) elements having valency zero
by at 2025-05-16 06:00:04